栈
栈是一种后入先出(LIFO)的线性逻辑存储结构。只允许在栈顶进行进出操作。
栈基本操作
基本操作包括:入栈(push)/出栈(pop)/获取栈顶元素(peek)。
栈的实现主要有两种:
- 数组实现,即顺序栈;
- 链表实现,即链式栈。
无论是以数组还是以链表实现,入栈、出栈的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
栈的应用比如函数执行/括号匹配/表达式计算/浏览器前进后退。
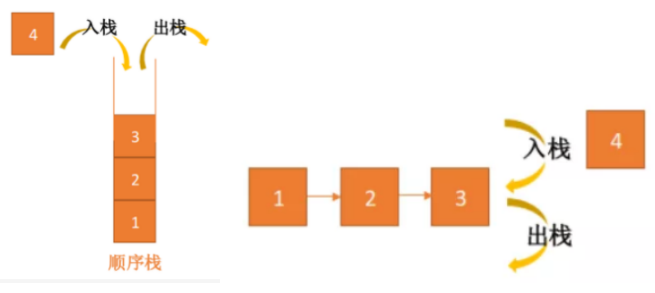
设计栈
1. 数组实现栈
// 数组栈
export default class ArrayStack<T> {
items: T[];
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
/**
* 入栈
* @param item
*/
push(item: T) {
this.items.push(item);
}
/**
* 出栈
* @returns
*/
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty) throw new Error('栈空');
return this.items.pop();
}
/**
* 获取栈顶元素
* @returns
*/
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty) throw new Error('栈空');
return this.items[this.size - 1];
}
/**
* 判空
* @returns
*/
get isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0;
}
/**
* 获取栈元素的个数
* @returns
*/
get size() {
return this.items.length;
}
}2. 链表实现栈
import LinkNode from '../../链表/设计链表/linkNode';
// 链表栈
export default class LinkStack<T> {
// 栈的长度
size: number;
// 栈顶指针
top: LinkNode<T> | null;
constructor() {
this.size = 0;
this.top = null;
}
/**
* 入栈
* @param item
*/
push(val: T) {
const node = new LinkNode(val);
if (this.isEmpty) {
// 栈空
this.top = node;
} else {
// 栈非空
node.next = this.top;
this.top = node;
}
this.size += 1;
}
/**
* 出栈
* @returns
*/
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty) {
// 栈空
throw new Error('栈空');
}
// 栈非空
const data = this.top!.val; // 栈顶元素值
this.top = this.top!.next; // 新栈顶
this.size -= 1;
return data;
}
/**
* 获取栈顶元素
* @returns
*/
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty) {
// 栈空
throw new Error('栈空');
}
return this.top!.val;
}
/**
* 判空
* @returns
*/
get isEmpty() {
return this.top === null;
}
}// 节点
export default class LinkNode<T> {
val: T;
next: LinkNode<T> | null;
constructor(val: T, next?: LinkNode<T> | null) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next ?? null;
}
}算法题
1. 包含 min 函数的栈
题目描述:定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈的最小元素的 min 函数在该栈中,调用 min、push 及 pop 的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
分析:
数据栈+最小栈法,利用一个最小栈存放当前数据栈的最小元素,保持两个栈的长度相同。从首个元素入数据栈开始,每个元素均入数据栈。同时,判断当前元素与最小栈栈顶元素的大小,将小的元素入最小栈即可。
求解:
// 数据栈+最小栈法
class MinStack {
dataStack: number[];
minStack: number[];
constructor() {
this.dataStack = [];
this.minStack = [];
}
push(x: number): void {
const dataSize = this.dataStack.length;
const minSize = this.minStack.length;
if (dataSize === 0 || this.minStack[minSize - 1] > x) {
this.minStack.push(x);
} else {
this.minStack.push(this.minStack[minSize - 1]);
}
this.dataStack.push(x);
}
pop(): void {
const dataSize = this.dataStack.length;
if (dataSize) {
this.minStack.pop();
this.dataStack.pop();
}
}
top(): number {
const dataSize = this.dataStack.length;
if (dataSize) {
return this.dataStack[dataSize - 1];
}
return NaN;
}
min(): number {
const minSize = this.dataStack.length;
if (minSize) {
return this.minStack[minSize - 1];
}
return NaN;
}
}2. 栈的压入、弹出序列
题目描述:输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如,序列 {1,2,3,4,5} 是某栈的压栈序列,序列 {4,5,3,2,1} 是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但 {4,3,5,1,2} 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
分析:
辅助栈模拟法,借用一个辅助栈 stack ,模拟压入/弹出操作的排列。根据是否模拟成功,即可得到结果。首先按照压栈序列的顺序执行辅助栈入栈操作,每次压栈序列中的元素入栈时,若栈不为空且栈顶元素等于弹出序列当前应弹出元素,即对栈进行出栈操作并更新弹出元素,最终判断栈是否为空即可。
求解:
// 辅助栈模拟法
export default function validateStackSequences(pushed: number[], popped: number[]): boolean {
const stack: number[] = [];
const size = pushed.length;
// 弹出序列当前应该弹出元素的下标
let poppedIndex = 0;
// 出栈和入栈序列不全为空
for (let i = 0; i < size; i += 1) {
const element = pushed[i];
// 将入栈序列元素入栈
stack.push(element);
while (stack.length && stack[stack.length - 1] === popped[poppedIndex]) {
// 栈不为空 且 栈顶元素等于弹出序列当前应弹出元素
stack.pop();
// 下一个应该弹出元素的下标
poppedIndex += 1;
}
}
return stack.length === 0; // 弹出与压入对应说明满足
}队列
队列是一种先入先出(FIFO)的线性逻辑存储结构。只允许在队首进行出队(即 delete 删除)操作,队尾进行入队(即 insert 插入)操作。
队列基本操作
队列的基本操作包括:入队 (enqueue)/ 出队 (dequeue)/ 获取队头元素(peek)
队列的实现主要有两种:
- 数组实现,即顺序队列。
- 链表实现,即链式队列。
无论是以数组还是以链表实现,入队、出队的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
队列的应用比如线程池、资源池、消息队列、异步队列。
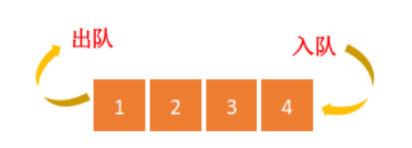
设计队列
1.顺序队列
数组实现,使用shift出队时每次都要移动队列元素,效率不高。改进方案是可以队列初始化时就需要规定队列长度,通过判断队尾是否有空间,有就让元素一直入队,直到队尾没有空间位置,然后进行整体进行一次搬移,这样优化了入队的效率,平均时间复杂度还是 O(1)。
// 数组实现顺序队列
export default class ArrayQueue<T> {
items: T[];
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
/**
* 入队
* @param item
*/
push(item: T) {
this.items.push(item);
}
/**
* 出队
* @returns
*/
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) throw new Error('队列空');
return this.items.shift();
}
/**
* 获取队顶元素
* @returns
*/
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) throw new Error('队列空');
return this.items[0];
}
/**
* 判空
* @returns
*/
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
/**
* 获取队元素的个数
* @returns
*/
getSize() {
return this.items.length;
}
}2.循环队列
数组实现,初始化需指定队列容量,留一个空位,队空条件 head = tail,队满条件 head =( tail + 1) % capacity,队列元素个数 (tail - head + capacity) % capacity。
// 数组循环队列
export default class LoopQueue {
// 存放元素的数组
values: (number | undefined)[];
// 当前元素个数
count: number;
// 队的长度
capacity: number;
// 队尾
head: number;
// 队尾
tail: number;
constructor(capacity: number) {
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.count = 0;
this.values = new Array(capacity);
}
/**
* 入队
* @param item
*/
enQueue(val: number) {
if (this.isFull()) {
throw new Error('队满');
}
this.values[this.tail] = val;
this.tail = (this.tail + 1) % this.capacity;
this.count += 1;
return true;
}
/**
* 出队
* @returns
*/
deQueue(): number {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error('队空');
}
const value = this.values[this.head] as number;
this.values[this.head] = undefined;
this.head = (this.head + 1) % this.capacity;
this.count -= 1;
return value;
}
/**
* 获取队头元素
* @returns
*/
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error('队空');
}
const value = this.values[this.head];
return value;
}
/**
* 判空
* @returns
*/
isEmpty() {
// 或 return this.head === this.tail
return this.count === 0;
}
/**
* 判满
* @returns
*/
isFull() {
// 或 return this.head === (this.tail + 1) % this.capacity
return this.count === this.capacity - 1;
}
/**
* 获取队元素的个数
* @returns
*/
getSize() {
return this.count;
}
/**
* 清空队列
* @returns
*/
clear() {
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
this.count = 0;
this.values = new Array(this.capacity);
return true;
}
}3.链式队列
链表实现,链表尾入队,链表头出队。
import LinkNode from '../../链表/设计链表/linkNode';
// 链表顺序队列
export default class LinkQueue<T> {
// 队的长度
size: number;
// 队尾指针
head: LinkNode<T> | null;
// 队尾指针
tail: LinkNode<T> | null;
constructor() {
this.size = 0;
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
/**
* 入队
* @param item
*/
enQueue(val: T) {
const node = new LinkNode(val);
if (this.size === 0) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
this.tail!.next = node;
this.tail = this.tail!.next;
}
this.size += 1;
}
/**
* 出队
* @returns
*/
deQueue() {
if (this.size === 0) {
// 队空
throw new Error('队空');
} else {
// 队非空
const node = this.head;
this.head = node!.next;
this.size -= 1;
return node!.val;
}
}
/**
* 获取队头元素
* @returns
*/
peek() {
if (this.size === 0) {
// 队空
throw new Error('队空');
} else {
return this.head!.val;
}
}
/**
* 判空
* @returns
*/
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0;
}
/**
* 获取队元素的个数
* @returns
*/
getSize() {
return this.size;
}
}// 节点
export default class LinkNode<T> {
val: T;
next: LinkNode<T> | null;
constructor(val: T, next?: LinkNode<T> | null) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next ?? null;
}
}算法题
1. 两个栈实现队列
题目描述:用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
分析:
栈用数组模拟,队列只允许在队首进行出队(即delete/pop删除 )操作,队尾进行入队(即insert/push插入)操作,因此其中一个栈 stack1用于入队,另一个栈stack2用于出队,出队时判断出队栈 stack2 是否为空:
- 空则将入队栈 stack1 中的元素全部转移至出队栈 stack2,然后出队栈 stack2 栈顶元素出队即可。
- 非空,则出队栈 stack2 栈顶元素直接出队。
求解:
// 数组模拟
class CQueue {
pushStack: number[];
popStack: number[];
constructor() {
this.pushStack = [];
this.popStack = [];
}
appendTail(value: number): void {
this.pushStack.push(value);
}
deleteHead(): number {
if (this.pushStack.length === 0 && this.popStack.length === 0) {
// 队列为空
return -1;
}
// 出队的栈为空时,依次将入队的栈中元素先入出队的栈
if (this.popStack.length === 0) {
while (this.pushStack.length) {
this.popStack.push(this.pushStack.pop()!);
}
}
return this.popStack.pop()!;
}
} Silver Bullet
Silver Bullet